Are you looking for a WordPress theme cheat sheet that will help you quickly modify your theme or create a new custom theme? WordPress has many built-in tools called template tags. You can use them to make your work easier. In this article, we will share with you a WordPress theme cheat sheet that is for beginners.
Want to stay ahead with AI-driven WordPress insights and stay updated with the latest trends? Subscribe for daily search insights at wpguidepro to improve your WordPress strategy!
Table of Contents
Before Getting Started
WordPress comes with a powerful templating system that allows theme developers to create beautiful designs for WordPress websites. WordPress themes are paid as well as free, which you can install on your website.
Every WordPress theme has some customization options. With the help of these options, you can change the colors, add a header image, set up menus and do a lot more.
But still, you can make changes only to the extent of options provided by the theme. Sometimes you may want to make small changes which are done through coding. In this case, you have to learn a little PHP, HTML and CSS.
First of all, you should understand how WordPress works in the background and what are WordPress theme cheat sheet templates.
After that, there are some best methods which you should follow. Like, creating a child theme so that you do not change the original theme files directly.
You can also practice on the theme by installing WordPress on your computer.
Now let’s start the WordPress theme cheat sheet for beginners.
Basic WordPress Theme Templates
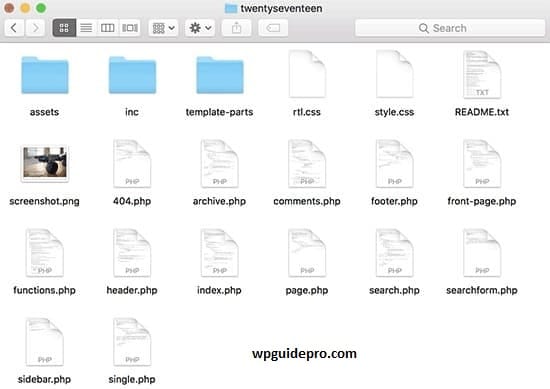
Every WordPress theme cheat sheet is made up of different files which are called templates. Every WordPress theme cheat sheet has a stylesheet and an index file. But usually a theme has many other files.
Below is a list of basic files which are present in every theme:
style.css
header.php
index.php
sidebar.php
footer.php
single.php
page.php
comments.php
404.php
functions.php
archive.php
searchform.php
search.php
If you want to create your own theme then you can start with WordPress theme cheat sheet. These wordpress theme cheat sheet come with ready-to-use files and CSS, so you can easily start creating your theme.
Template Tags in Header
WordPress has many useful functions that you can use in different parts of the theme. These functions are called template tags.
The first and probably the most important function that is required in every standard WordPress theme is called wp_head. This function looks like this:
<?php wp_head(); ?>This code contains all the important HTML that WordPress needs to add to the head section of every page. This function is very important for the WordPress plugins to work properly.
Below are some important template tags that you may often see or use in your theme’s header.php file. But you can use them in any part of your theme when needed.
// Shows the name of your blog or website
<?php bloginfo('name'); ?>
// Example Output: wpguidepro
// Shows the title of the current page
<?php wp_title(); ?>
// Example Output: Home, About Us, Contact
// Displays the exact URL of your website
<?php bloginfo('url'); ?>
// Example Output: https://wpguidepro.com
// Displays the site's tagline or short description
<?php bloginfo('description'); ?>
// Example Output: Best WordPress Guides for Beginners
// Shows the URL of your current theme folder
<?php bloginfo('template_url'); ?>
// Example Output: https://wpguidepro.com/wp-content/themes/your-theme
// Direct link to your style.css file
<?php bloginfo('stylesheet_url'); ?>
// Example Output: https://wpguidepro.com/wp-content/themes/your-theme/style.css
// Shows the RSS Feed URL of your site
<?php bloginfo('rss2_url'); ?>
// Example Output: https://wpguidepro.com/feed
// Displays the Pingback URL (used for comment communication)
<?php bloginfo('pingback_url'); ?>
// Example Output: https://wpguidepro.com/xmlrpc.php
// Shows your current WordPress version
<?php bloginfo('version'); ?>
// Example Output: 6.5.2Template Tags Used in Other Theme Files
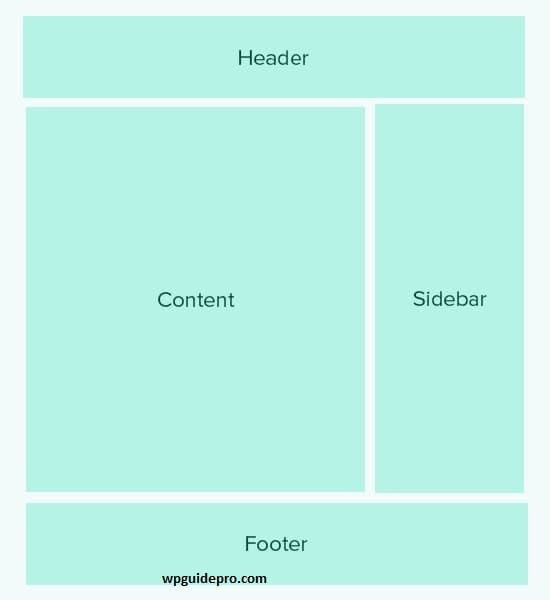
For example, your theme’s index.php file uses these tags to include important parts of the website such as header, footer, content, comments, and sidebar.
// Displays the content from Header.php file
<?php get_header(); ?>
// Example: This shows the top part (header) of every page on wpguidepro
// Displays the content from Footer.php file
<?php get_footer(); ?>
// Example: This shows the bottom part (footer) of every page on wpguidepro
// Displays the content from Sidebar.php file
<?php get_sidebar(); ?>
// Example: This shows the sidebar area with widgets or info on wpguidepro
// Displays the content from Comments.php file
<?php comments_template(); ?>
// Example: This shows the comments section below blog posts on wpguidepro
// Displays the full content of the post
<?php the_content(); ?>
// Example: Shows the full article or blog post on wpguidepro
// Displays a short summary (excerpt) of the post
<?php the_excerpt(); ?>
// Example: Used in blog listings to show a preview of each post
// Displays the title of the post
<?php the_title(); ?>
// Example: Shows the heading or name of the blog post
// Displays the link to the post
<?php the_permalink(); ?>
// Example: The full URL to open that specific post
// Displays the category of the post
<?php the_category(', '); ?>
// Example: Shows which category the post belongs to (like “SEO”, “Tips”)
– Displays the name of the post’s author
<?php the_author(); ?>
// Example: Shows who wrote the post
// Displays the unique ID number of the post
<?php the_ID(); ?>
// Example: Internal number WordPress uses to identify the post
// Shows the edit link for logged-in users who can edit posts
<?php edit_post_link(); ?>
// Example: Only visible to admins/editors when they are logged in
// Displays the link to the next post
<?php next_post_link('%link'); ?>
// Example: Link that takes you to the newer post
// Displays the link to the previous post
<?php previous_post_link('%link'); ?>
// Example: Link that takes you to the older postWordPress themes have areas where widgets can be added. These areas are called sidebars. These are the parts of the theme files where users can add WordPress widgets by drag and drop.
Usually a theme has more than one place where widgets can be added. But in most cases these widget areas are on the right or left side of the theme layout.
If you want to explore in more detail then check out our guide which explains how you can add dynamic widget ready sidebars to your WordPress theme.
The code that is used to show the sidebar in your theme is given below:
<?php
// Check if wpguidepro's sidebar is active
if ( ! is_active_sidebar( 'wpguidepro-sidebar' ) ) {
return; // If no widgets, stop here
}
?>
<aside id="wpguidepro-sidebar" class="widget-area" role="complementary">
<?php dynamic_sidebar( 'wpguidepro-sidebar' ); ?>
</aside><!-- #wpguidepro-sidebar -->WordPress lets you make menus to help people move around your website.
A theme can have more than one menu spot.
To learn how to make your own menu, see our guide on creating custom menus in WordPress.
Below is the code you can use in your theme to show a menu.
<?php
wp_nav_menu( array(
'theme_location' => 'wpguidepro-menu',
'container_class' => 'wpguidepro-menu-style'
) );
?>Theme location depends on the name that your theme used when registering the navigation menu.
You can name the CSS container class anything you like.
This is the main element of your navigation menu, so that you can style the menu according to your design.
Miscellaneous Template Tags
Below are some important tags that you often use in your WordPress theme.
<?php
/**
* WPGuidePro Code Snippets for Theme Development
* Helpful template tags for WordPress developers.
*/
/**
* Display the date when the current post was published
*/
echo '<p><strong>Published on:</strong> ' . get_the_date() . '</p>';
/**
* Display the date and time the current post was last modified
*/
echo '<p><strong>Last Modified on:</strong> ' . get_the_modified_time('F d, Y') . '</p>';
/**
* Display the featured image (post thumbnail)
*/
if ( has_post_thumbnail() ) {
echo '<div class="wpguidepro-featured-image">';
the_post_thumbnail('large');
echo '</div>';
}
/**
* Display monthly archives
*/
echo '<div class="wpguidepro-archives">';
wp_get_archives([
'type' => 'monthly',
'limit' => 12,
'format' => 'html',
]);
echo '</div>';
/**
* Display a list of categories
*/
echo '<ul class="wpguidepro-categories">';
wp_list_categories([
'title_li' => '',
'show_count' => true,
]);
echo '</ul>';
/**
* Display Gravatar for a specific email address
* (Change email@example.com to your target email)
*/
echo '<div class="wpguidepro-gravatar">';
echo get_avatar('email@example.com', 32);
echo '</div>';
/**
* Display Gravatar of the current post author
*/
echo '<div class="wpguidepro-author-gravatar">';
echo get_avatar(get_the_author_meta('ID'), 32);
echo '</div>';
?>Conditional Tags in WordPress Themes
Conditional tags are functions that check whether a condition is correct or not. They always give two answers: True or False.
You can use these tags in your WordPress theme or plugin. They check whether a task or condition is being completed or not. If the condition is correct then you can get some work done, otherwise you can show something else.
Example: If the current post has a featured image then it is fine. But if there is no featured image, then you can show the default image.
<?php
// WPGuidePro: Featured Image Checker
if ( has_post_thumbnail() ) {
the_post_thumbnail(); //
} else {
echo '<img src="' . get_stylesheet_directory_uri() . '/assets/images/wpguidepro-default-thumb.jpg" alt="WPGuidePro Default Thumbnail" />';
}
?>Below are some more conditional tags you can use.
// Checks if a single post is being displayed
is_single()
// Checks if a page is being displayed
is_page()
// Checks if the main blog page is displayed
is_home()
// Checks if a static front page is displayed
is_front_page()
// Checks if current viewer is logged in
is_user_logged_in()WordPress Loop
Loop is a part of the code that WordPress uses to display posts. Whenever a blog post, news or any content is displayed on the website, it is displayed with the help of a loop.
Many template tags of WordPress work only within the loop, because they depend on the data of the post or post type.
<?php
if (have_posts()) :
while ( have_posts() ) : the_post();
?>
<h2 id="post-<?php the_ID(); ?>"><a href="<?php the_permalink() ?>" rel="bookmark" title="Permanent Link to <?php the_title(); ?>"><?php the_title(); ?></a></h2>
<p class="date-author">Posted: <?php the_date(); ?> by <?php the_author(); ?></p>
<?php the_content(); ?>
<p class="postmetadata">Filed in: <?php the_category(); ?> | Tagged: <?php the_tags(); ?> | <a href="<?php comments_link(); ?>" title="Leave a comment">Comments</a></p>
<?php
endwhile;
// If no posts were found
else :
?>
<p>Sorry no posts matched your criteria.</p>
<?php
endif;
?>