If you want your WordPress website to look different and stylish from others, then customizing the theme is the easiest way. This transforms your site from a boring template into a website that truly showcases your brand.
But before making changes, it is important to understand one thing: each file controls a different part of the website. For example, changing the header design, setting the footer layout a little, or changing the look of blog posts there are separate files for everything.
In this guide, you will learn how to find the right files edit wordpress and how to edit it safely so that the site does not crash.
And by the end you will have a clear plan on how to edit the theme files, plus you will also get some bonus tips on how to add custom code without messing up the theme files.
Want to stay ahead with AI-driven WordPress insights and stay updated with the latest trends? Subscribe for daily search insights at wpguidepro to improve your WordPress strategy.
Table of Contents
Understanding Theme Template Files Edit wordpress
WordPress themes are created through a system called template hierarchy. This system consists of separate files that decide how which parts of the website should look. Each file has its own work and controls the design and features of the site.
Template Hierarchy System
WordPress follows a simple order when a visitor comes to your site. For example, if someone opens a blog post, WordPress checks the files in this order:
- single-{post-type}-{slug}.php
- single-{post-type}.php
- single.php
- singular.php
- index.php
Due to this order, even if one file is missing, WordPress displays the content.
Important Template Files
Every WordPress theme has some common files that you must know:
- index.php
- header.php
- footer.php
- single.php
- page.php
- archive.php
- functions.php
Finding Template Files Edit WordPress Theme
To find the right file, you need to understand where the files are and which file controls what.
Ways to access theme files:
Go to File Manager or FTP: /wp-content/themes/your-theme-name/. You can edit files directly here, but you need some technical knowledge. The risk is also high.
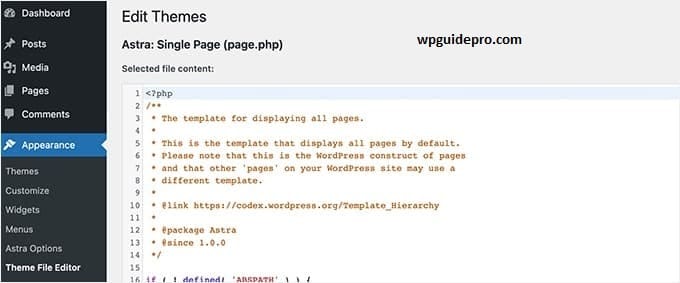
Go to WordPress Dashboard: Appearance > Theme Editor. You can edit directly from here, but it is not a safe option for beginners.
Edit on Local Computer: Best and safe option is to download the files, edit them in the code editor on your computer and then upload them back.
Which file controls what?
You need to check which file controls which page or element. To check this, you can use these methods:
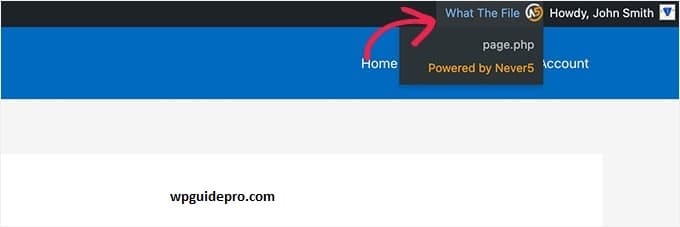
Plugins: install What The File or Theme Check. This plugin tells which template the current page is using.
Browser Tools: Right-click > Inspect Element. Here, the HTML structure and CSS classes give you an idea of which file it is.
Theme Docs: check your theme’s documentation or support forum. Good themes provide details.
Common Changes That Logs Make
Header Change: You can add logo, menu or extra code in header.php.
Footer Change: You can add/change copyright text, social links, widgets in footer.php.
Blog Post Layout: You can change post title, author box, comments, related posts in single.php.
Homepage: You can customize homepage by editing front-page.php, home.php or index.php (depends on theme).
Archive Pages: The layout of categories, tags and date archives changes in archive.php.
Making changes in a safe way
Before making direct edits on the live site, follow these steps:
Create a backup Use plugins like UpdraftPlus or BackWPup.
Create a staging site where you can test without affecting the live site.
Use a child theme so that your changes remain safe even after updates.
Bonus Tip: Adding Custom Header and Footer Code in WordPress
Instead of editing theme files directly, WordPress has some safer options where you can add your custom code, especially in the header and footer.
WordPress Hooks
WordPress has action hooks through which you can add code without touching the theme files:
- wp_head hook to add code in the head section (use functions.php or a custom plugin).
- wp_footer hook to add code before the closing body tag.
The advantage of this method is that your changes are safe even after the theme is updated, and the risk of site breaking is reduced.
Header and Footer Plugins
If you want to avoid coding then using plugins is the best option:
Insert Headers and Footers: simple plugin where you can easily add scripts, meta tags and tracking codes.
Code Snippets: for adding PHP, CSS and JavaScript code with error checking.
Custom CSS and JS: gives a separate section for CSS and JS code with syntax highlighting.
Child Theme Method
If you want a professional and long-term solution then child theme is the best option:
- Create a new folder in /wp-content/themes/ with the name of your child theme.
- Create style.css file and write the info of parent theme in it.
- Create functions.php file and add custom functions.
Copy any file from the parent theme and put it in the child theme folder and edit it.
The biggest benefit of the child theme is that your customizations remain safe even after the parent theme is updated.
FAQs: Which Files to Edit in Your WordPress Theme
What will happen if wrong template files edit wordpress?
If you edit the wrong file, those changes may not show up on the site. But the site will not break unless you make any coding error. Always keep a backup and test the changes on a staging site.
Can I edit theme files directly from the dashboard?
Yes, WordPress has a built-in editor. But it is not a safe option for beginners, as it does not have things like syntax check and auto-backup. It is better to edit on FTP or local computer.
How will I know that there are custom template files in the theme?
Premium themes often keep their own custom files in addition to WordPress default files. Check your theme’s file list or documentation to understand the structure.
What if changes disappear after theme update?
This happens when you edit parent theme files directly. The solution is to use child theme. With child theme your changes remain safe even after update.
Is it safe to edit functions.php file?
functions.php is a powerful file but a little risky too. Even a small error can crash the whole site. Always keep backup, and if possible use child theme or plugin


