If you want to start your own blog, run an online store, or work on a website with a team, it is important to understand that each WordPress user roles has a different role in WordPress.
These roles are created so that you can easily decide who will do what. This not only keeps the website secure, but also ensures that each person gets to do only the work that he or she should do.
In this guide, we’ll explain in simple terms what each role does, how to set or change roles, and share some easy ways to effectively manage users.
By the end of the guide, you’ll know enough to build a smart system for your website that makes your work easy and secure.
Want to stay ahead with AI-driven in WordPress insights and stay updated with the latest trends? Subscribe for daily search insights at wpguidepro.com to improve your WordPress strategy.
Table of Contents
What Are WordPress User Roles and Permissions?
WordPress user roles and permissions define what each user can do on your website.
These tasks can range from small things to big things like writing posts, editing posts, or managing plugins and themes.
The advantage of this system is that only authorized people can access important areas.
WordPress has 6 main roles by default:
- Administrator
- Editor
- Author
- Contributor
- Subscriber
- Super Admin (this is only for multisite websites)
Each role has some set powers (permissions). Like:
- The Administrator has full control of everything.
- The Subscriber can only view the content, he cannot change any settings.
If you understand these roles well, then you can easily decide who has what responsibility without putting your website’s security at risk.

1. Administrator Role
Administrator role is the most powerful role in WordPress.
The person with this role has full control of the website.
The administrator can do the following:
- Can install or delete themes and plugins
- Can add new users, edit or delete them
- Can publish, edit or delete any post or page
- Can change the settings of the website
This role should only be given to a person whom you trust completely, because the administrator can even delete the entire site.
If you are running the website alone, you will be the default administrator.
When should you give the administrator role?
- To yourself (if you are the owner of the website)
- To the developer (if you need to fix or update the website)
- To a trusted business partner or co-founder
Best Advice:
Give administrator access to only a few people. The fewer the people in this role, the lesser the chance of any mistake or damage
2. Editor Role
The Editor role is for people who manage the content of the website, such as blog posts and pages.
The Editor can do the following:
- Can publish, edit, or delete any post or page
- Can check and approve or delete comments
- Can manage categories and tags
But the Editor cannot touch the website’s settings, plugins, or themes.
When should the Editor role be given?
This role should be given to those people who:
- Manage content
- Lead a team that has multiple writers (contributors or authors)
Best Tip
If many people are writing on your website, then the editor helps in maintaining good quality work on the website by checking the content of all of them without touching any technical thing
3. Author Role
Author role is a little less powerful than Editor.
Author can do these things:
- Can write his own post
- Can edit his own post
- Can publish (run) his own post
- Can even delete his own post
But Author cannot edit anyone else’s post.
And he cannot change the website’s settings or plugins either.
When should Author role be given?
This role should be given to those people who:
- Guest bloggers or freelance writers who want to handle their content themselves
- People who regularly (frequently) write on your site
Best Tip
Since the author can publish his post himself, you should check his content – so that only good and correct content appears on the website
4. Contributor Role
Contributor role is one level below Author, it has more restrictions.
Contributor can do these things:
- Can write your post
- Can edit your post
- Can send your post for review (cannot publish)
But Contributor cannot do these things:
- Cannot publish your post
- Cannot upload images or any media
- Contributor always needs help of an Editor or Administrator so that he can publish the post.
When should Contributor role be given?
This role is best for those people:
- New team members or interns
- People who occasionally write guest posts
Important thing
Contributor cannot put images in his post, so the Editor or Admin has to help in uploading media (images)
5. Subscriber Role
Subscriber role is the simplest role in WordPress.
Subscribers can do the following:
- They can create their own profile
- They can login and see only those things which are for registered users
- This role is mostly used for membership websites or newsletters.
When should the Subscriber role be given?
This role is best for people who:
- Users of websites with memberships
- People who visit the website daily and want to get updates
Best idea
Keep subscribers for functions that help in running the website, but do not require going into the website settings this keeps your site safe.
Bonus Super Admin Role
If you are running a multisite network of WordPress, then the Super Admin role is very important.
Super Admin can do the following:
- Can manage themes and plugins for all websites
- Can add or delete new websites in the network
- Can control the settings of the entire network
This role is only for those people who manage many websites simultaneously.
Do not give Super Admin to too many people, because in this role you have complete control over the entire network
How to Customize Existing User Roles and Permissions in WordPress
Sometimes WordPress’ default roles are not right for your needs. The good news is that you can change the permissions of these roles with the help of plugins. Such as User Role Editor or Members plugins.
Here’s how:
Install User Role Plugin
Install a plugin like User Role Editor, which will let you change roles and their permissions easily.
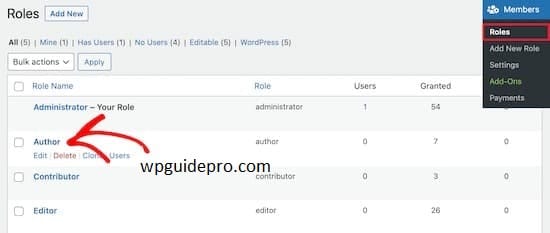
Change role permissions
Go to the plugin settings, choose the role you want to change, then add or remove permissions
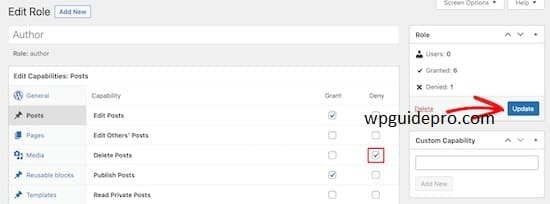
Save your changes
Once you’ve set the necessary permissions, save your settings and test the new roles.
By customizing roles, you can keep your website both flexible and safe
How to Create Custom User Roles in WordPress
If you want to create a completely new role, follow these steps:
Use a plugin
Just like customizing roles, creating a new role is also the easiest with plugins. User Role Editor or Members plugins are both good.
Name your role Give your new role a name, such as “Product Reviewer”.
Set the role’s permissions
Decide what users of this role can do, such as writing drafts but not publishing posts.
Save and test Always test your new role to make sure everything is working fine.
By creating a new role you can create a system according to the specific needs of your website, without compromising security.
Tips and Tutorials on WordPress User Role Management
Some important tips for role management:
- Assign roles to each person according to their need. Do not give more permissions than necessary.
- Check from time to time whether the roles and permissions are correct or not.
- Teach your team about their roles and train them if needed.
- For people in important roles like Administrator or Editor, turn on two-factor authentication (extra security).
If you want to explore more, there are good tutorials on WordPress.org, YouTube, or WordPress forums.


